HYDORELECTRIC DAMS
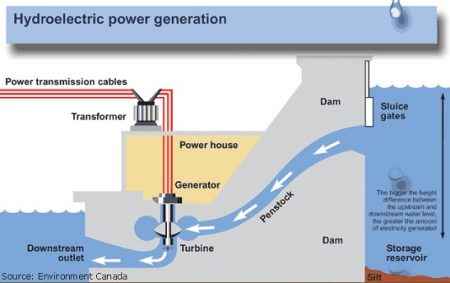
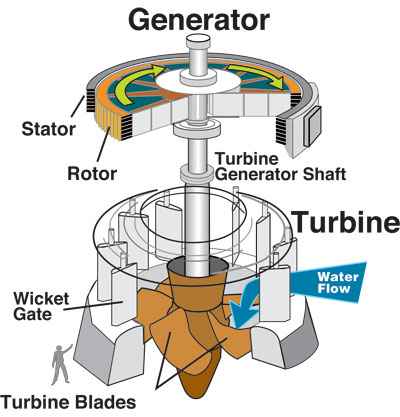
Hydroelectric dams produce electricity by using dammed water to turn turbines. By opening the dam’s sluices, falling water then turns propeller-like turbines, which then turns metal shafts in electric generators. It is the motor that produces electricity. In this case the energy extracted from the water depends on the volume and on the difference in height between the source and the water’s outflow.
Hydroelectricity produced by Hydroelectric dams is the most widely used form of renewable energy. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, the project produces no direct waste and has a considerably lower output level of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) than fossil fuel powered energy plants. Worldwide, hydroelectricity supplied an estimated 900 GWe in 2008. This was approximately 20% of the world’s electricity and accounted for about 88% of electricity from renewable sources.
Advantages
• Elimination of the cost of fuel.
• A hydroelectric plant is immune to increases in the cost of fossil fuels
• Longer economic lives
• Operating labor cost is low, plants are automated and have very few personnel on site during normal operation.
• Low construction cost when added to an existing dam
• Hydroelectric dams do not burn fossil fuels
• Does not produce directly carbon dioxide (greenhouse gas)
• Reservoirs created by hydroelectric schemes often provide facilities for water sports and become tourist attractions
Disadvantages
• Hydroelectric projects can be disruptive to surrounding aquatic ecosystems
• Fish livestock such as Salmon spawn can be harmed on their migration to sea when they must pass through turbines.
• Generation of hydroelectric power changes the downstream river environment.
• A dissolved oxygen content of the water may change from pre-construction conditions.
• In some cases, an entire river may need to be diverted leaving a dry riverbed.
• Reservoirs of power plants in tropical regions may produce indirectly greenhouse gases such as methane and carbon dioxide.
• Relocation of the nearby population may be required
• Dam failures are potentially serious
• Lives from the nearby population can be lost and historically and culturally important sites can be flooded and lost.
• Dams may be subject to enemy bombardment during wartime, sabotage, and terrorism.
• Changes in the amount of river flow will affect the operation
MAIN COMPONENTS of a HYDROELECTRIC DAM SYSTEM
• Storage Reservoir – which stores the dammed water
• Dam Structure – which dams the water
• Sluice Gates – which control the water flow
• Penstock – which is a tunnel structure leading the water to the turbines
• Turbines – which turn the generators when water flows through
• Generators – which produce the electricity when turned by the turbines
• Transformers – which transfer the produced electricity to the electricity grid
RELATED ARTICLES:
Alternative Energy – The Facts – Ocean Wave energy – Part 7
Alternative Energy – The Facts – Solar Power – Part 6
Alternative Energy – The Facts – Tidal Energy – Part 5
Alternative Energy – The Facts – Geothermal Energy – Part 4
Alternative Energy – The Facts – Solar Power – Part 3
Alternative Energy – The Facts – Wind Power – Part 2
Alternative Energy – The Facts – An Introduction Into Renewable Energy – Part 1