A complete Wind Turbine Glossary listing all major parts and components of an industrial wind turbine.
Anemometer: Measures the wind speed and transmits wind speed data to the controller.
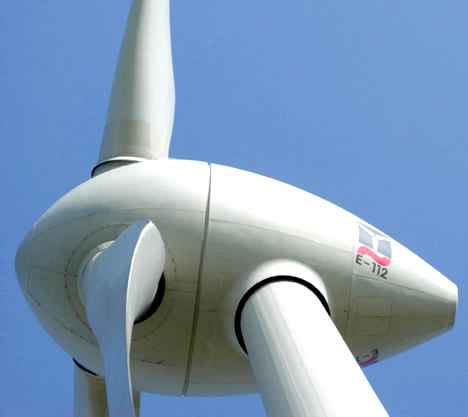
Blades: Most turbines have either two or three blades. Wind blowing over the blades causes the blades to “lift” and rotate.
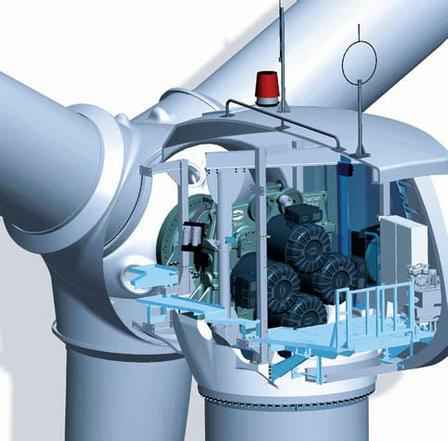
Brake: A disc brake which can be applied mechanically, electrically, or hydraulically to stop the rotor in emergencies.
Controller: The controller starts up the machine at wind speeds of about 8 to 16 miles per hour (mph) and shuts off the machine at about 65 mph. Turbines cannot operate at wind speeds above about 65 mph because their generators could overheat.
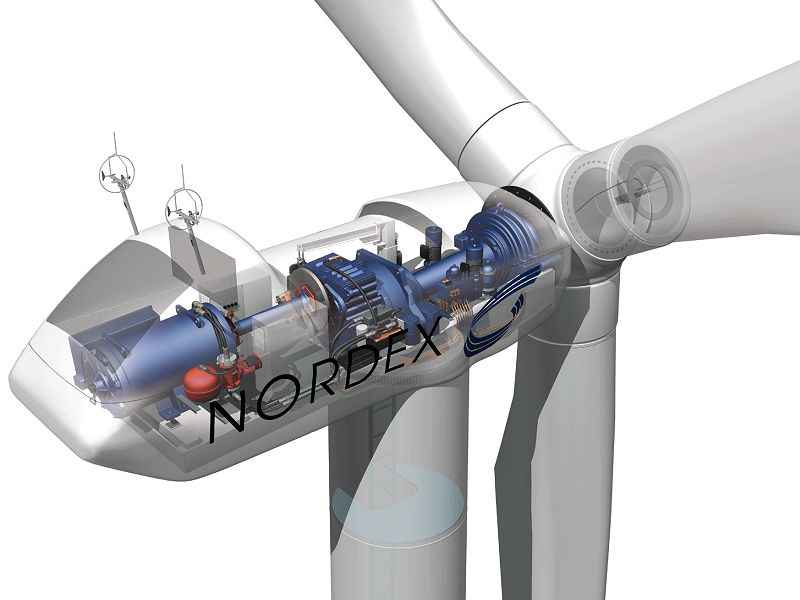
Gear box: Gears connect the low-speed shaft to the high-speed shaft and increase the rotational speeds from about 30 to 60 rotations per minute (rpm) to about 1200 to 1500 rpm, the rotational speed required by most generators to produce electricity. The gear box is a costly (and heavy) part of the wind turbine and engineers are exploring “direct-drive” generators that operate at lower rotational speeds and don’t need gear boxes.
Generator: Usually an off-the-shelf induction generator that produces 50-cycle AC electricity. 
Low-speed shaft: The rotor turns the low-speed shaft at about 30 to 60 rotations per minute.
Nacelle: The rotor attaches to the nacelle, which sits atop the tower and includes the gear box, low and high-speed shafts, generator, controller, and brake. A cover protects the components inside the nacelle. Some nacelles are large enough for a technician to stand inside while working.
Pitch: Blades are turned, or pitched, out of the wind to keep the rotor from turning in winds that are too high or too low to produce electricity.
Rotor: The blades and the hub together are called the rotor.
Tower: The tower supports the nacelle and is most often a steel cylinder with an internal access ladder which provides access for maintenance and repairs. Because wind speed increases with height, taller towers enable turbines to capture more energy and generate more electricity.
Transformer: At the base of the tower there is a transformer that alters the voltage of the electricity generated so that it can be fed into the local electricity network.
Wind direction: Some turbines are “upwind” turbines, so-called because they operate facing into the wind. Other turbines are designed to run “downwind”, facing away from the wind.
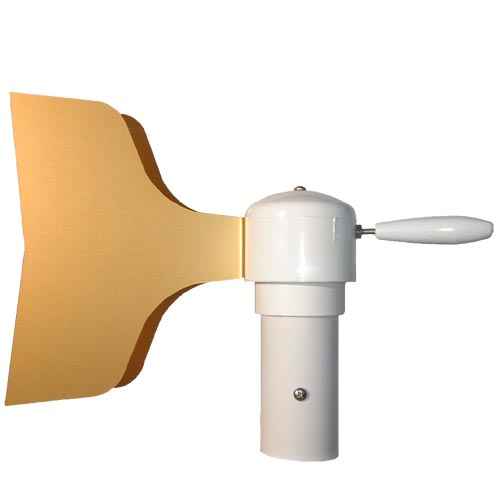
Wind vane: Measures wind direction and communicates with the yaw drive to orient the turbine properly with respect to the wind.
Yaw drive: Upwind turbines face into the wind; the yaw drive is used to keep the rotor facing into the wind as the wind direction changes. Downwind turbines don’t require a yaw drive, the wind blows the rotor downwind.
Yaw motor: Powers the yaw drive.
Related Articles:
Top 50 Green Companies of the World Related Articles about Wind Power Companies Building My Own Small Wind Turbine Saves Money Every Day
Watch This Dynamic Video!

If you’re in the market for a wind turbine please contact us. Turbines from 200w to 20kw and up. Price ranges from $849(200w) to $1.900,000.00 (1500KW) .Complete systems are sold and shipped from Canada or directly from our manufacturer worldwide.
To see our range of products click here.
Installation teams for large systems are available for installation in any part of the world. Project managers assigned by us to lead and train local teams to install, run and maintain turbines or entire wind farms. Local teams acquire required machines, cranes and electricians all under the guidance of our project managers.
Post Your Comment or Read Great Comments Below
[bestwebsoft_contact_form]
















As the most stable country to do business within Latin America, Chile is proving to be a launching ground for renewable energy. We look at the progress and requirements of investing in wind farms within the country.