TIDAL ENERGY
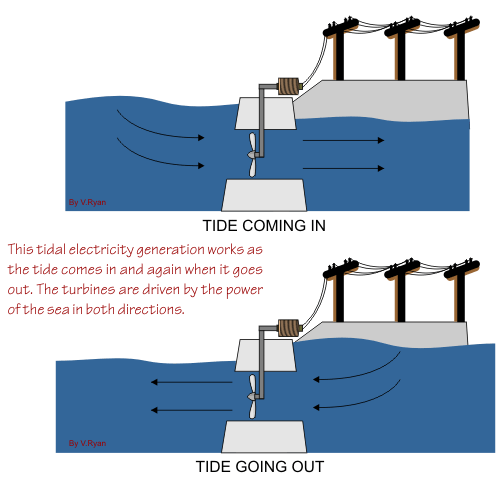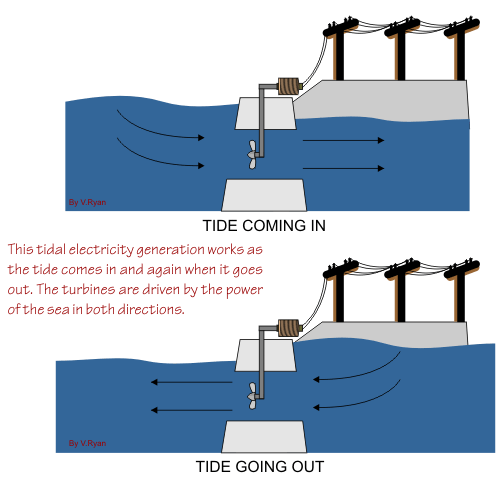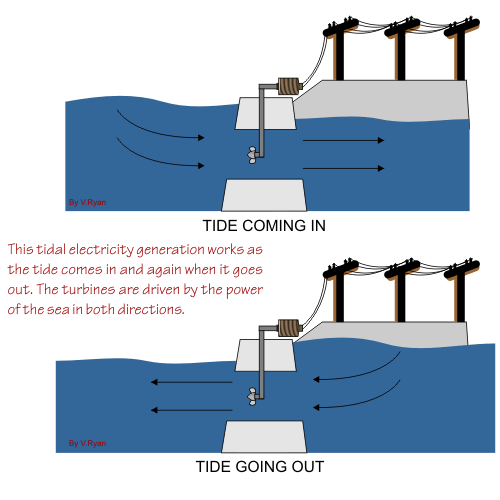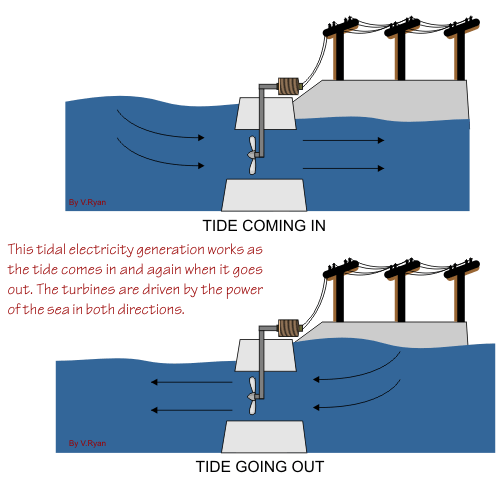
Even the power of the tides can be harnessed to produce electricity. Similar to the more conventional hydroelectric dams, the tidal process utilizes the natural motion of the tides to fill reservoirs, which are then slowly discharged through electricity-producing turbines. The former USSR produced 300 MW in its Lumkara plant using this method.
Advantages
• Tides rise and fall every day in a very consistent pattern.
• Economic life of a tidal power plant. A plant is expected to be in production for 75 to 100 years
• Tidal energy does not require any fuel.
• It reduces the dependence upon fossil fuels
• Tidal and wave energy is free, renewable, and clean source of energy
• It produces clean electricity, with no production of greenhouse gas or pollution.
• Tidal and wave energy generation and consumption creates no liquid or solid pollution
• Highly efficient resource (compared with coal and oil at 30%, tidal power efficiency is about 80%)
• Energy capturing and conversion mechanism may help protect the shoreline
• Energy capturing and conversion mechanism has little visual impact
• About 60 billion watts of energy from tides can be used for electricity generation
• Tides are active 24 hours a day, 365 days a year
• Tidal power is a renewable source of energy.
• It produces energy for free, once the initial costs are recovered.
Disadvantages
• The altering of the ecosystem
• Damages through reduced flushing, winter icing and erosion can change the vegetation of the area and disrupt the balance.
• Only available in a small number of regions.
• Requires a basin or a gulf that has a mean tidal amplitude (the differences between spring and neap tide) of at least 7 meters or above.
• It leads to the the displacement of wild life habitats.
• It can only be used where there is suitable tidal flow or wave motion. So it can not be used inland.
• It only produces electricity during tidal surges.
• Barrage systems require salt resistant parts and lots of maintenance.
• The frames of the turbines can disrupt the movement of large marine animals and ships through the channels on which the barrage is built.
• The barrage systems have the disadvantages of disrupting fish migration and killing fish passing through the turbines, therefore, there is also the risk of destruction of ecosystem that rely on the coming and going of tides.
• The ecosystem is disrupted during the construction of building the tidal fence. This affects the fishes and also the fishermen who depends their life on it.
• Tidal energy can only be created on a coast with a good tidal differential. Worthless for a landlocked country, has to be converted to something else to be transported
• It is limited because the tide never speeds up or slows down, and occurs on 6 hour cycles.
• The cost for constructing and running the facility
• Construction of strong, cheap and efficient conversion devices may be problematic

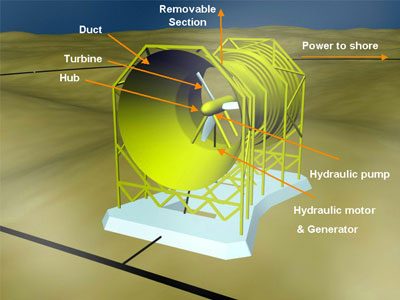
Main Components of a Tidal Energy Plant
• A Tidal Containment Wall – encloses an interior body of water
• The Piles – which the secure the Support Columns to the sea bed
• The Panels – which separate the Artificial Tidal Lagoon from the surrounding ocean
• Locking Posts which secure the Panels to the Support Columns.
• Turbines – which turn its motion caused by the tidal waves into electricity
To be continued in Part 6 – Solar Power (Solar Panels) – click here!
Related Articles:
Alternative Energy – The Facts – Ocean Wave energy – Part 7
Alternative Energy – The Facts – Solar Power – Part 6
Alternative Energy – The Facts – Tidal Energy – Part 5
Alternative Energy – The Facts – Geothermal Energy – Part 4
Alternative Energy – The Facts – Solar Power – Part 3
Alternative Energy – The Facts – Wind Power – Part 2
Alternative Energy – The Facts – An Introduction Into Renewable Energy – Part 1
Back to MyWindPowerSystem homepage click here!





got a stream 7.81cfs what would you recomend 43 feet of vertical drop thanks for any info lg
7.81 csf 43 feed vertical drop in a stream do you have anything that would help generate energy stream runs 700 feet to get the 43 feet thanks lg